
Logos from Mythos: The Heart of Eurasian Philosophy
At some level, a religious tradition can be thought of as distinguished by, or even defined by, its creation story – i.e. its cosmological narrative - and the Hindu/Vedic tradition is no different in this regard although it has many nuances…

Indo-European Philosophy: On the Soul
There are many parallels that can be drawn between early Hellenic and Upanishadic philosophy. In particular, we find many similarities between the philosophy presented by Plato in his Middle Period as he developed and fine-tuned his theory…
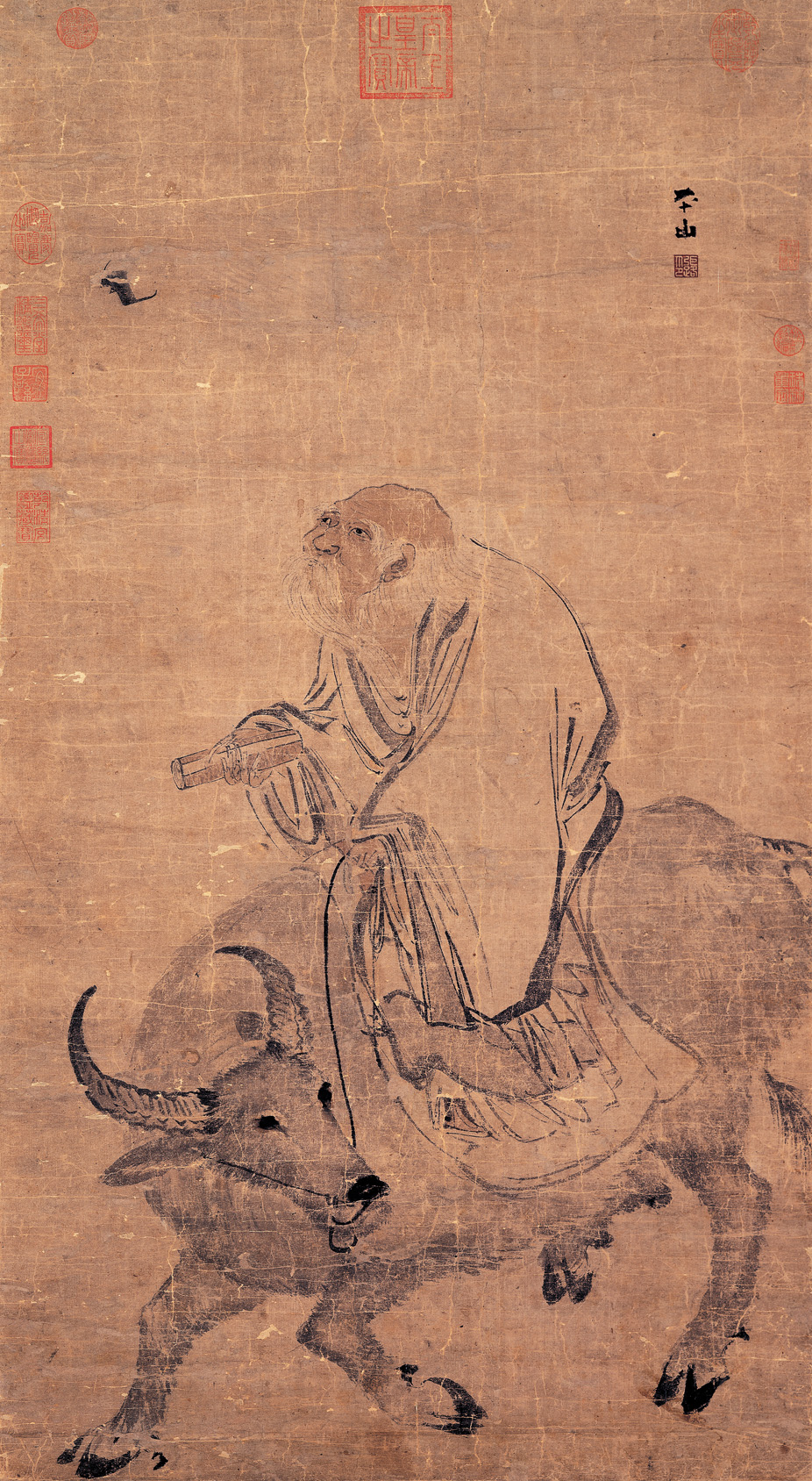

The Lǎozǐ and Zhuangzi: Daoism and the Way of Virtue
As the Confucian school was referred to as Rújiā, the Daoist school was referred to as Daojiā, each called out as one of the six main philosophical schools during the Warring States Period to the Early/Former Han. While a Daoist “canon”…
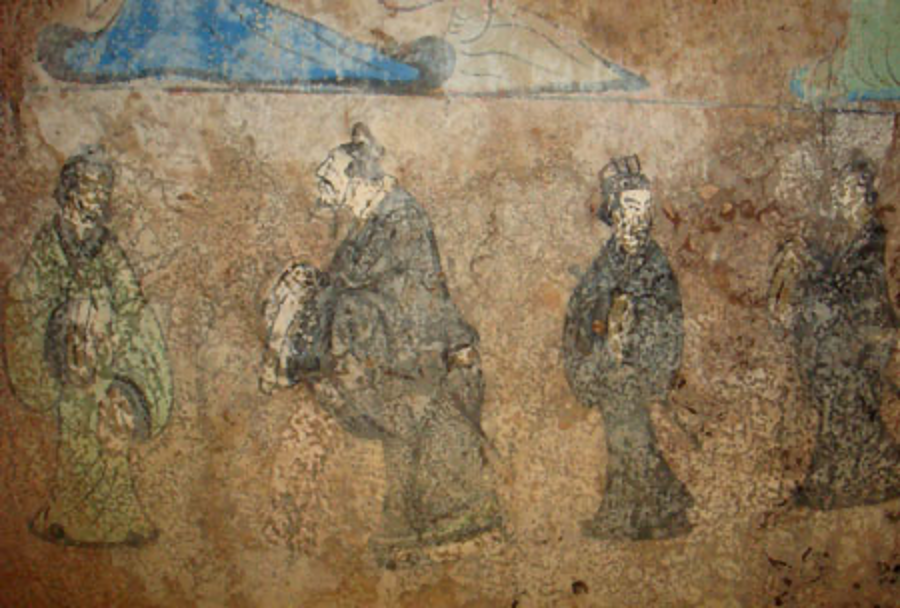

Early Chinese Philosophy: The Humanism of Confucius
The classical period of ancient Chinese philosophy runs from about the 6th century BCE till the 2nd century BCE and is marked by the proliferation and flowering of many varying philosophical schools, an era in Chinese history referred to (by…
Plato and the Allegory of the Cave: Ideas, Being and Becoming
The first systematic treatment of philosophy, and arguably the most influential, in the West can be found in works of Plato, in particular in his works the Phaedo, the Republic and the Timaeus which are by most accounts the most influential…
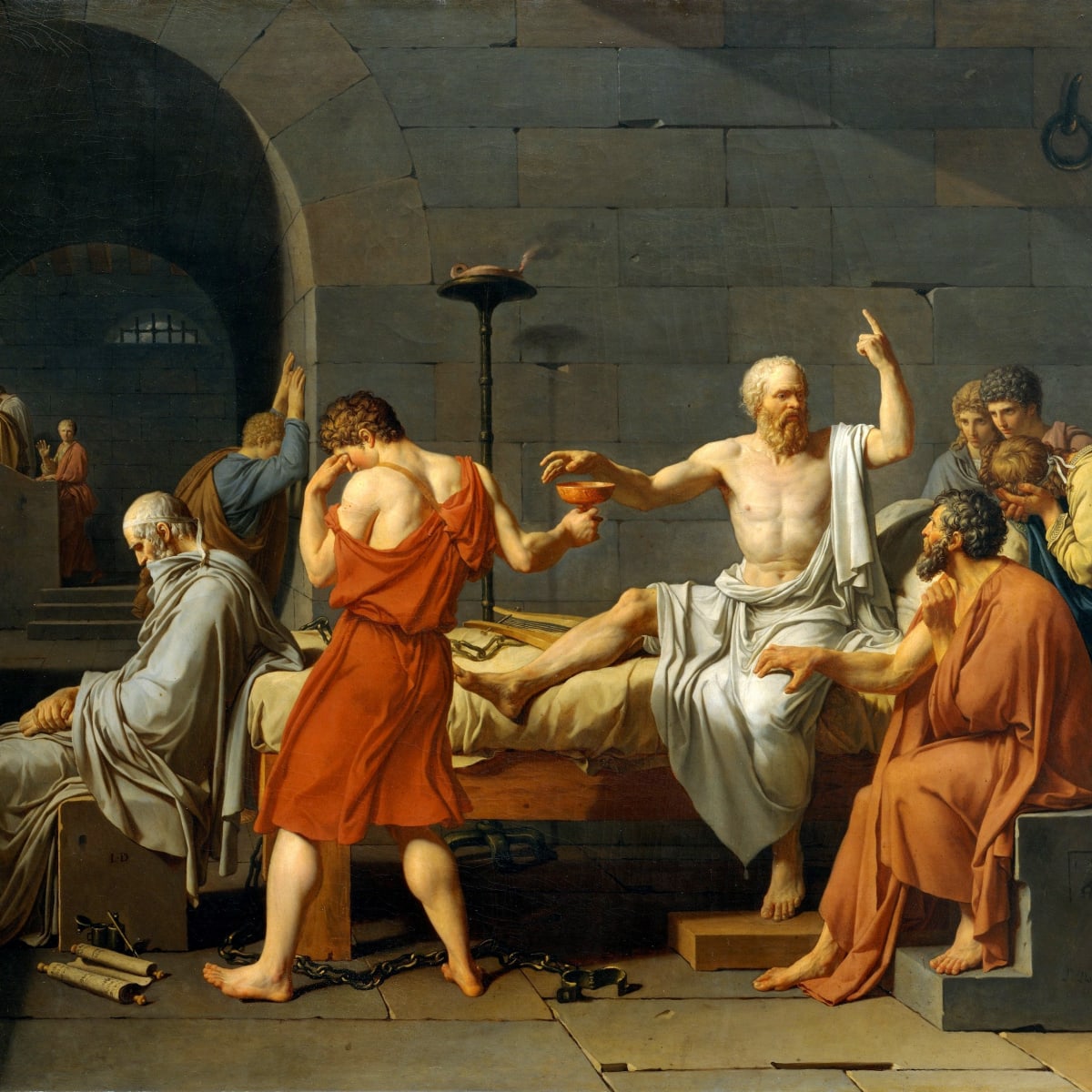

The Legacy of Socrates: Skepticism, Knowledge and Reason
One of the best indications of the influence of Socrates on the development of Western philosophy, what the Hellenes, or Greeks, termed philosophia, his ideas being primarily represented by the writings of his best known pupil Plato, is the…
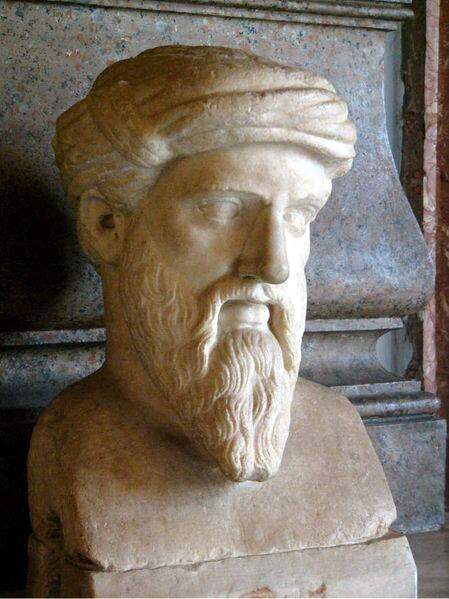

Pythagoras: The Father of Hellenic Philosophy
Pythagoras, Thales of Miletus, Parmenides, Heraclitus, Xenophanes, Zeno, Empedocles, Anaxagoras, Leucippus, and Democritus all made contributions to Pre-Socratic philosophical thought and were referenced by later philosophers and historians…

Buddhist Philosophy: Impermanence, Suffering and the “No-Self”
Running parallel to the maturation and evolution of Hellenic philosophy, to the East the Indo-Aryan people were going through a similar intellectual revolution from the prevalence of ritual and ceremonial worship of gods and goddesses embedded…
Upanishadic Philosophy: Brahmavidyā and the Soul
Orthodox Indian philosophy, the legacy of the Indo-Aryans, takes on a much different form than it does in the West, and in turn a much different form that it does in the Far East, despite the fact that the intellectual developments – if we…

The Metaphysics of the I Ching: The Alignment of Heaven, Man and Earth
While the translational difficulties from Traditional Chinese into English are fairly well documented, even with the introduction of the Pinyin Romanization system of Chinese words in the middle of the twentieth century which is now predominantly…
