
The Reductionist West and Ancient Wisdom
Modern science tells us that what we can truly say about empirical reality only has relative (Relativity) or statistical significance (Quantum Mechanics), Quantum Theory in particular calling into question the role of the observer[1] but each…

Chinese Monotheism: Worship of Heaven (Shangdi)
Hinduism, Buddhism, Confucianism and Taoism (Daoism), all rich and prolific theo-philosophical traditions of the East which thrived in ancient times and still flourish today, were and are much more accepting of the worship of many different…

Confucian Philosophy in Antiquity
Confucius (c. 551 – 479 BCE) stands alongside Laozi as one of the great independent Chinese philosophers in antiquity, supposedly having consulted Laozi on some aspects of funeral rights and being impressed with his insight, or so the tradition…
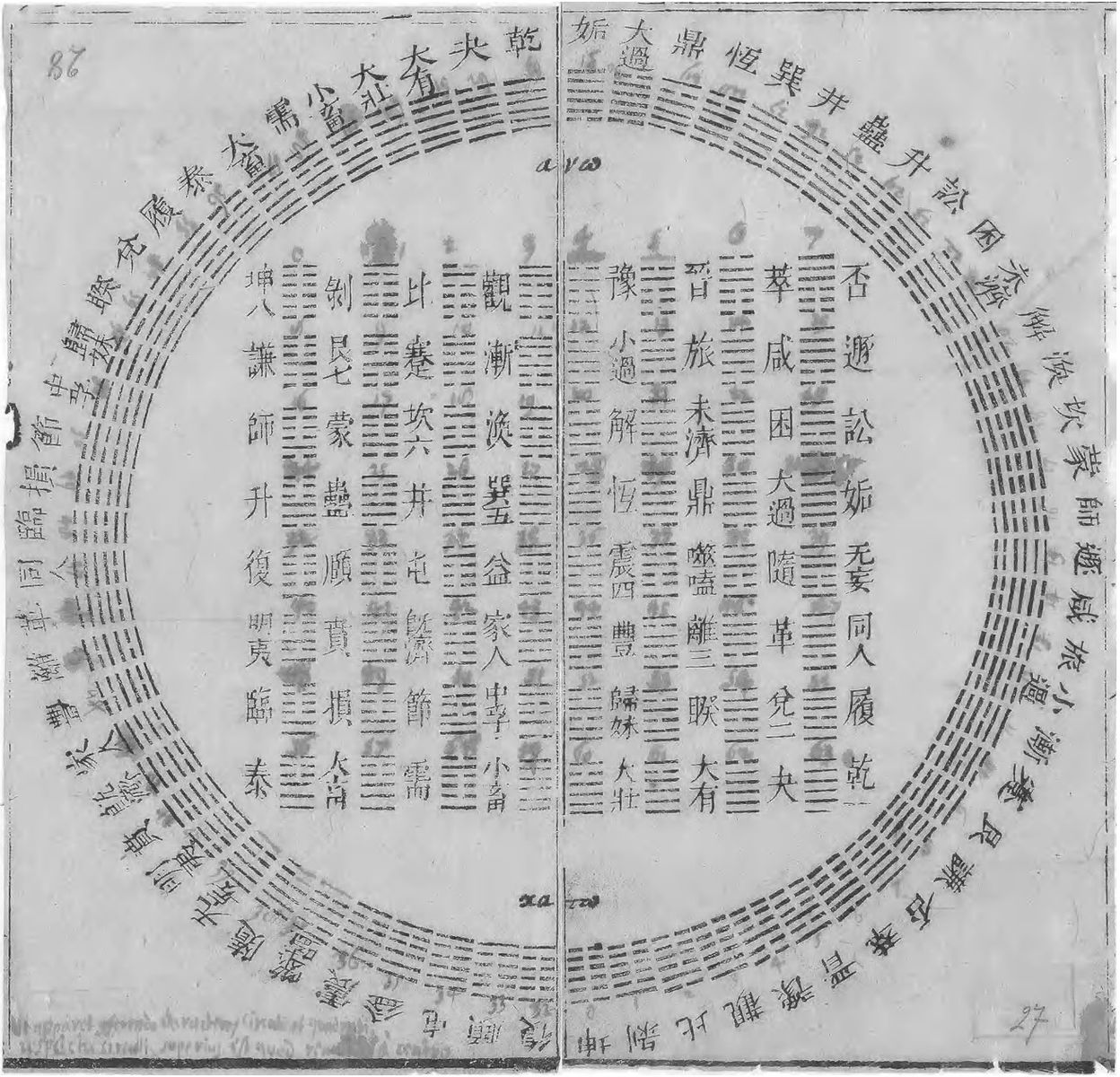
Divination in the I Ching
Divination, omens, portents etc. was a common practice throughout all of the ancient world in fact. As already mentioned we see the practice, and its relationship with the priestly class not only in ancient Greece but most certainly ancient…
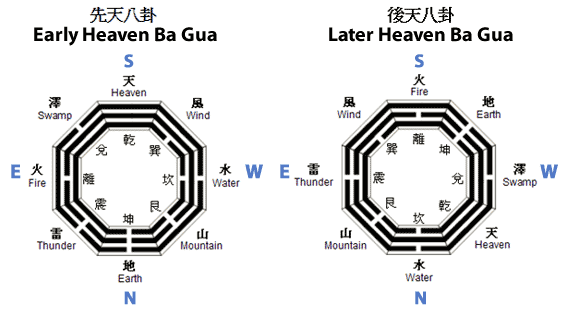
The Book of Changes: The Wisdom of the Far East
One of the most unique, lasting and influential texts that has come down to us from the Far East that in antiquity is the Yijing (I Ching), also known as the Book of Changes. The work has a long history, its roots dating back at least to Bronze…
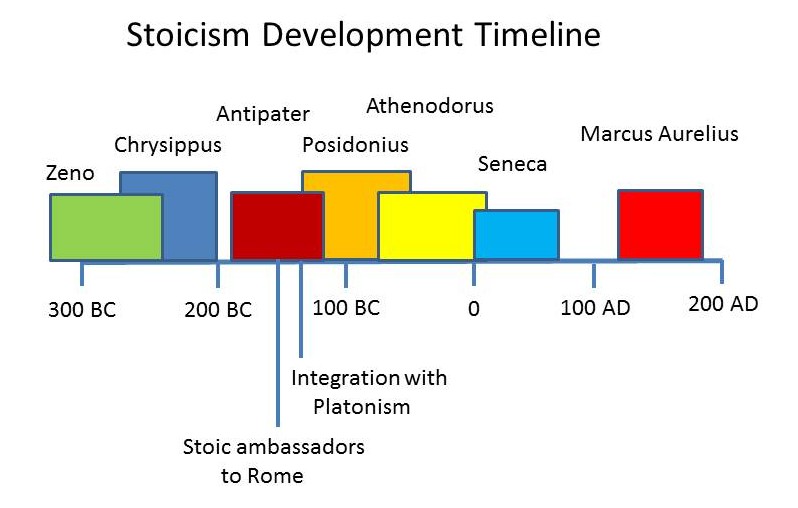
Stoic Philosophy in Antiquity: Its Origins, Metaphysics and Ethical Principles
Introduction
Consistent across all of the Hellenistic philosophical schools was the importance of the Soul, the distinction of the human soul as having the capability to reason (what came to be known as logos, a very important term in early…

What is Vedanta?
Introduction
The ancient Indo-Aryan civilization sprung forth in the Indus valley region in modern day India and Pakistan (to the ancients Eastern Persia), and was the source of the “Vedas”, some of the oldest extant literature of mankind.…
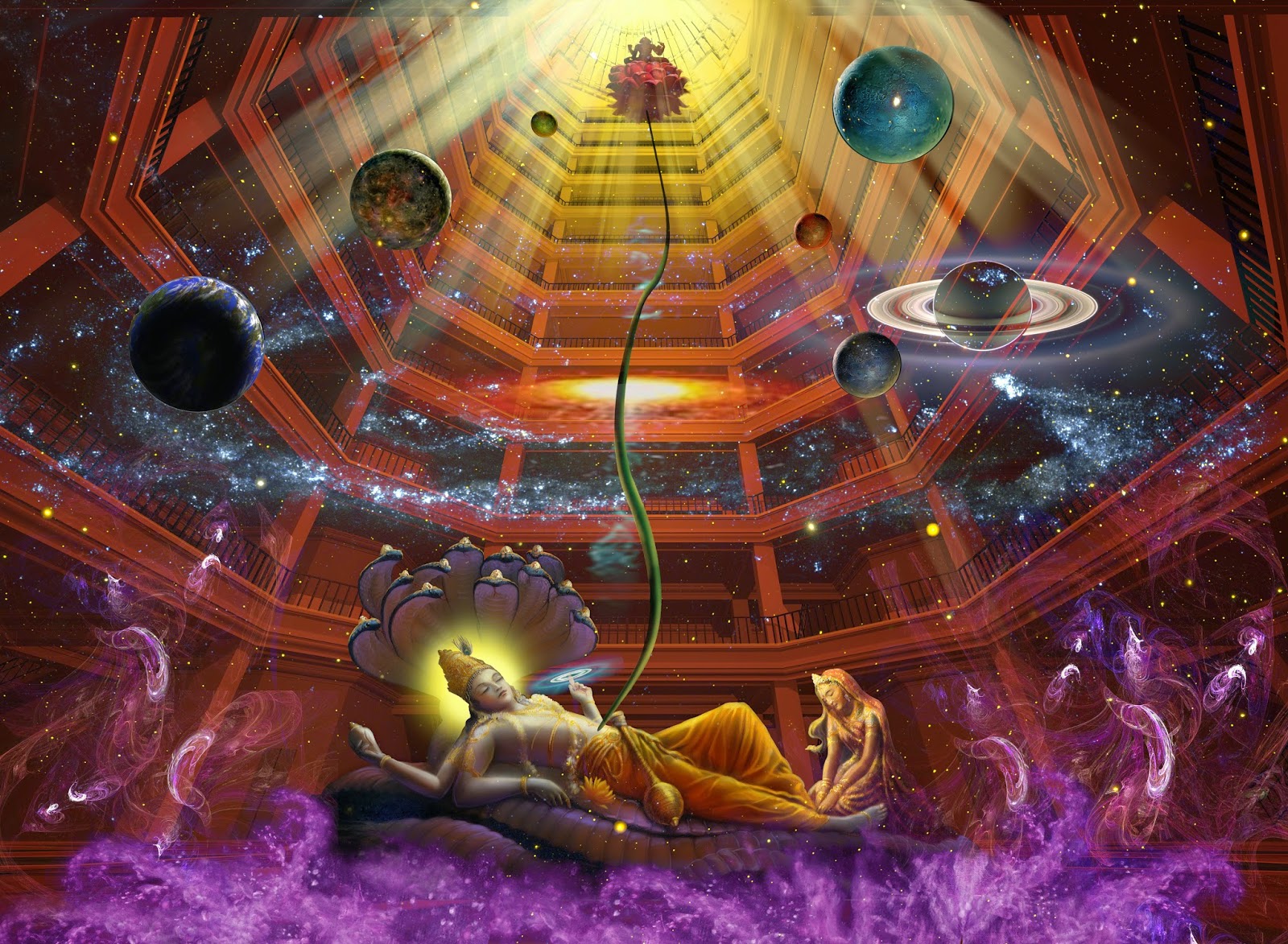

Vedic Cosmological Narratives (Part II)
The Hymn of Purusha: God Takes Shape[1]
While the preceding passage from the Rig Veda contains some of the root kernel philosophical elements of Vedic philosophy, there is another passage from the same collection of hymns dating back to the…

Vedic Creation Narratives and Philosophy: Brothers in Arms (Part I)
When looking at the Indo-Aryan tradition, given its age and maturity and its fundamental belief and faith in the unity of man and the universe from which he emerged (unique to the Eastern religious traditions in general), a line can be drawn…

The Philosophy of the East: The Legacy of the Indo-Aryans
Introduction
Throughout academic parlance in the Enlightenment Era intellectual and philosophical development throughout mankind’s history has been divided into Eastern and Western branches. The Eastern branch of thought and development…
